Folliculitis
Folliculitis is inflammation of one or more hair follicles. It can occur anywhere on the skin.
Causes
Folliculitis starts when hair follicles are damaged by rubing from clothing, blockage of the follicle, or shaving. Most of the time, the damaged follicles become infected with Staphylococcus (staph) bacteria.
Barber's itch is a staph infection of the hair follicles in the beard area of the face, usually the upper lip. Shaving makes it worse. Tinea barbae is similar to barber's itch, but the infection is caused by a fungus.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is a disorder that occurs mainly in black men. If curly beard hairs are cut too short, they may curve back into the skin and cause inflammation.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include a rash, itching, and pimples or pustules near a hair follicle in the neck, groin, or genital area. The pimples may crust over.
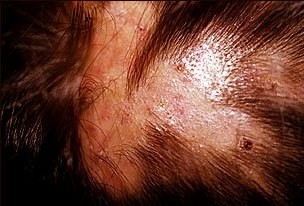
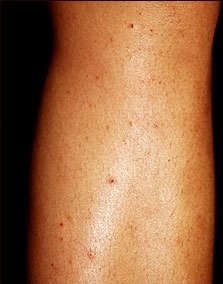
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can diagnose this condition by looking at your skin. Lab tests may show which bacteria or fungus is causing the infection.
Treatment
Hot, moist compresses may help drain the affected follicles.
Treatment may include:
- Antibiotics applied to the skin (mupirocin) or taken by mouth (dicloxacillin)
- Antifungal medications to control the infection
Outlook (Prognosis)
Folliculitis usually responds well to treatment, but may come back.
Possible Complications
Folliculitis may return or spread to other body areas.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Apply home treatment and call your health care provider if your symptoms:
- Come back often
- Get worse
- Last longer than 2 or 3 days
Prevention
To prevent further damage to the hair follicles and infection:
- Reduce friction from clothing
- Avoid shaving the area if possible (if shaving is necessary, use a clean, new razor blade or an electric razor each time)
- Keep the area clean
- Avoid contaminated clothing and washcloths
Source: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000823.htm

