Hand-foot-mouth disease
Contents
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Hand-foot-mouth disease is a relatively common infection viral infection that usually begins in the throat.
A similar infection is herpangina.
Causes
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) is most commonly caused by coxsackievirus A16, a member of the enterovirus family.
The disease is not spread from pets, but it can be spread by person to person. You may catch it if you come into direct contact with nose and throat discharges, saliva, fluid from blisters, or the stools of an infected person. You are most contagious the first week you have the disease.
The time between infection and the development of symptoms is about 3 - 7 days.
The most important risk factor is age. The infection occurs most often in children under age 10, but can be seen in adolescents and occasionally adults. The outbreaks occur most often in the summer and early fall.
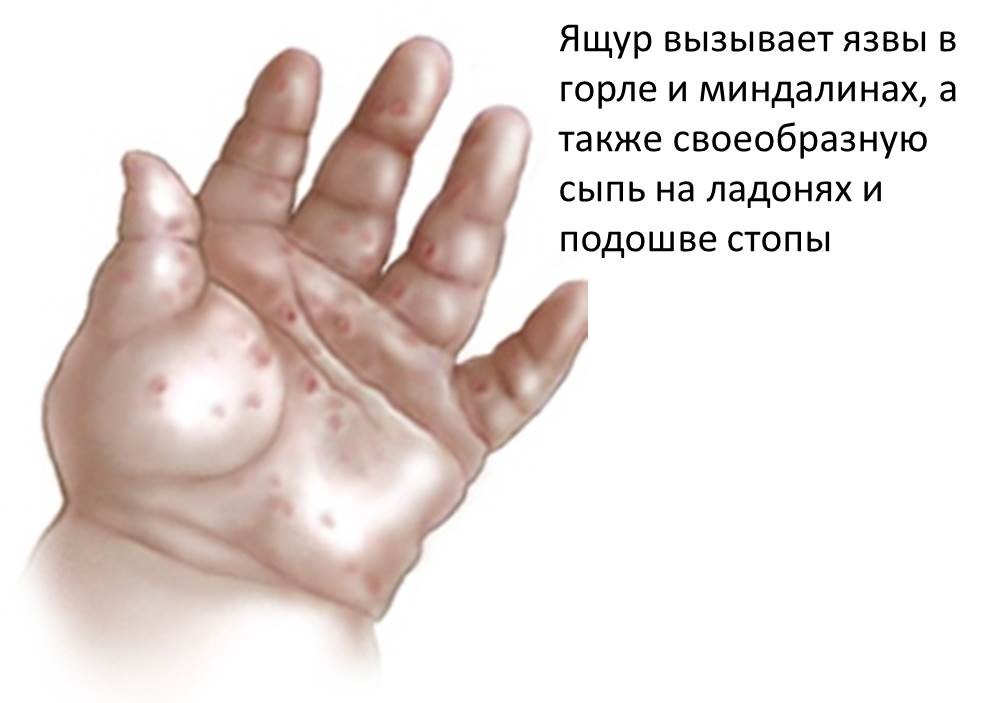
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a viral infection caused by Coxsackievirus that usually begins in the throat. Symptoms include; fever, sore throat, ulcers in the throat, headache, and a rash with blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
Symptoms
- Fever
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Rash with very small blisters on hands, feet, and diaper area; may be tender or painful if pressed
- Sore throat
- Ulcers in the throat (including tonsils), mouth, and tongue
Exams and Tests
A history of recent illness and a physical examination, demonstrating the characteristic vesicles on the hands and feet, are usually sufficient to diagnose the disease.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for the infection other than relief of symptoms.
Treatment with antibiotics does not work and is not recommended. Over-the-counter medicines, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen can be used to treat fever. Aspirin should not be used in viral illnesses in children under age 12 years.
Salt water mouth rinses (1/2 teaspoon of salt to 1 glass of warm water) may be soothing if the child is able to rinse without swallowing. Make sure your child gets plenty of fluids. Extra fluid is needed when a fever is present. The best fluids are cold milk products. Many children refuse juices and sodas because their acid content causes burning pain in the ulcers.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Generally, complete recovery occurs in 5 to 7 days.
Possible Complications
- Dehydration
- Febrile seizures
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if there are signs of complications, such as pain in neck or arms and legs. Emergency symptoms include convulsions.
You should also call if:
- Medicine does not lower a high fever
- Signs of dehydration occur:
- Dry skin and mucus membranes
- Weight loss
- Irritability
- Lethargy
- Decreased or dark urine
Prevention
Avoid contact with people with known illness. Always wash your hands well and often, especially if you are in contact with people who are sick.
Alternative Names
Coxsackievirus infection

